Introduction
SEO is crucial for online visibility. It’s how search engines like Google understand and rank websites. This guide will break down SEO into its core components: on-page, off-page, and technical optimization. We’ll also explore specialized areas like local and e-commerce SEO. Get ready to learn how to improve your website’s ranking and attract more visitors
SEO is essential for online success. It increases your website’s visibility on search engine results pages (SERPs), making it easier for potential customers to find you. A higher ranking often translates to increased organic traffic, which can lead to more leads, sales, and brand awareness. Essentially, SEO helps you reach your target audience effectively and efficiently.
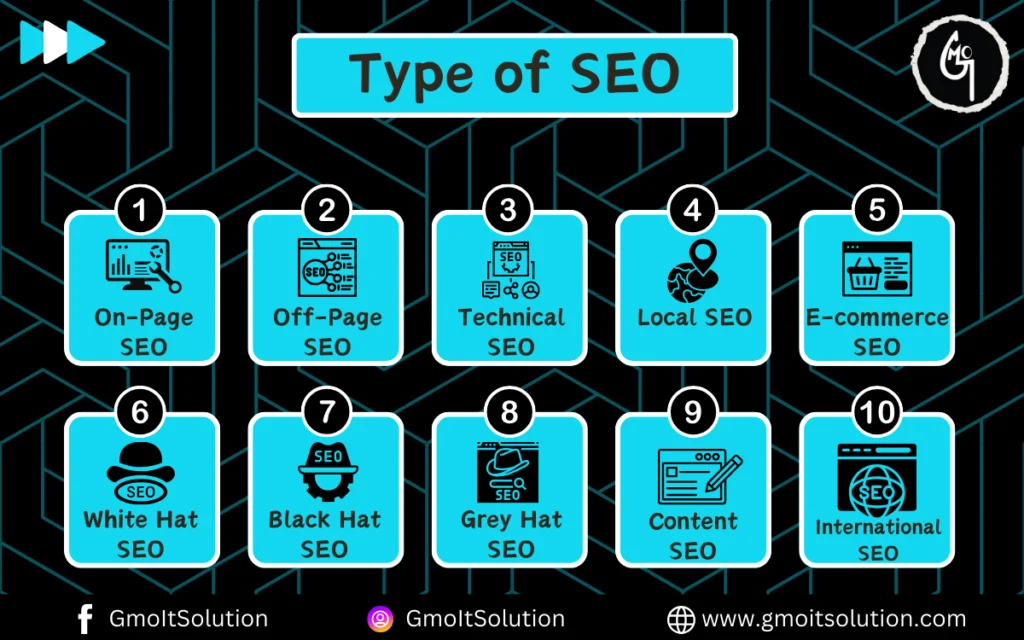
To achieve optimal search engine rankings, we’ll explore several key types of SEO:
On-Page SEO
On-page SEO notes for methods and strategies to use within your website to improve your website’s search engine rankings. This includes optimizing elements on your site to make it more attractive to search engines and users.
Key Elements:
Title Tags
The title of your web page that shows in search engine results and browser tabs.
Example: For a blog about healthy recipes, a title tag might be “10 Healthy Recipes for Quick and Easy Meals.”
Meta Descriptions
A short summary of a webpage’s content is shown under the title tag in search results.
Example: “Discover easy and nutritious recipes for busy weeknights. Quick tips and delicious ideas to keep your meals healthy.”
Header Tags
Tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.) are used to define headings and subheadings within your content.
Example: An H1 tag could be “Ultimate Guide to Home Gardening,” with H2 tags like “Benefits of Home Gardening” and “Essential Tools for Gardening.”
Keyword Optimization
Adding relevant keywords to your content to match search queries.
Example: Using keywords like “vegan recipes” in a recipe blog post that targets users searching for plant-based meal ideas.
Content Quality
It is creating valuable, engaging, and informative content that answers consumer questions.
Example: An in-depth article on “How to Improve Your Sleep Hygiene” with tips, research, and practical advice.
Image Optimization
Optimizing images by using descriptive filenames and alt text to help search engines understand the content.
Example: An image of a “freshly baked apple pie” might have the filename “apple-pie.jpg” and the alt text “Delicious homemade apple pie.”
Internal Linking
Linking to other pages or posts within your website to help users navigate your site and help search engines index it.
Example: Within a blog post on “Best Yoga Poses,” you might link to another post about “Yoga for Beginners.”
Off-Page SEO
Off-Page SEO focuses on improving your website’s visibility and authority through activities outside your site. This includes building backlinks, engaging in social media marketing, listing your site in online directories, and collaborating with influencers. By enhancing your site’s reputation and establishing connections across the web, Off-Page SEO helps boost your search engine rankings and drive more traffic to your site.
Key Elements:
Link Building
Getting backlinks from other websites to increase credibility and authority.
Example: Getting a link to your blog from a well-known industry website.
Social Media Marketing
Promote content through social media platforms to increase traffic and engagement.
Example: Sharing a blog post on Facebook and Twitter to reach a large audience.
Online Directories
Listing your website in relevant online websites to improve visibility and credibility.
Example: Submitting your business to Yelp or Yellow Pages.
Guest Posting
Writing articles for other blogs or websites to gain liability and backlinks.
Example: Contributing a guest post to a popular marketing blog with a link back to your site.
Influencer Marketing
Partnering with influencers to promote your content or products.
Example: Collaborating with a social media influencer to review your product.
Brand Mentions
Increasing mentions of your brand across the web, even without direct links.
Example: Getting featured in industry news or being mentioned in online forums.
Technical SEO
Technical SEO involves optimizing the technical aspects of your website to improve its performance and search engine visibility. This includes ensuring fast page load times, mobile-friendliness, proper indexing, and efficient crawling. Key elements also include creating XML sitemaps, managing robots.txt files, and implementing structured data. By addressing these technical factors, you help search engines easily crawl and understand your site, leading to better rankings and user experience.
Key Elements:
Website Speed
Ensuring your site loads quickly to better user experience and ranking.
Example: Using tools like “Google PageSpeed Insights” to analyze and improve page load times.
Mobile-Friendliness
Make sure your site is optimized for mobile devices.
Example: fulfilling a responsive design that adjusts to various screen sizes.
XML Sitemaps
Creating a file that helps search engines understand the structure of your site.
Example: Submitting an XML sitemap to Google Search Console.
Robots.txt
A file that instructs search engines on which pages to crawl and index.
Example: Blocking search engines from indexing a test page with a robots.txt entry like “Disallow: /test-page.”
Structured Data
Using schema markup to help search engines understand your content better.
Example: Adding schema for reviews to help display star ratings in search results.
Crawl Budget
Managing how search engines crawl and index your site’s pages.
Example: classifying important pages for crawling while minimizing duplicate content.
Indexation
make sure your pages are properly indexed by search engines.
Example: Checking for crawl errors in Google Search Console and fixing them.
Tools: Google Search Console, Screaming Frog SEO Spider, GTmetrix.
Local SEO
Local SEO focuses on optimizing your website to attract more business from local searches. It involves optimizing your Google My Business listing, ensuring consistent business information across online directories, and encouraging customer reviews. Local SEO helps your business appear in local search results and maps, making it easier for nearby customers to find and visit your location.
Key Elements:
Google My Business Optimization
announcing and optimizing your Google My Business listing for local visibility.
Example: Adding exact business details, and photos, and responding to reviews on your Google My Business profile.
Local Citations
Make sure your business is listed correctly in various online directories.
Example: Listing your business on Yelp, Yellow Pages, and local chamber of commerce websites.
Online Reviews
Encouraging and managing customer reviews to build trust and improve rankings.
Example: Ask your satisfied customers to leave positive reviews on Google or Yelp.
Local Directories
Being listed in local-specific directories and platforms.
Example: Submitting your business to local directories like Angie’s List or local blogs.
Geo-Targeting
Using location-specific keywords and content to attract local customers.
Example: A restaurant might use keywords like “best Italian restaurant in Chicago.”
Best Practices: Keep NAP (Name, Address, Phone Number) consistent across all platforms, use local keywords, and engage with local community events.
E-commerce SEO
E-commerce SEO involves optimizing online stores to improve their visibility in search engines and drive traffic and sales.
Key Elements:
Product Page Optimization
Ensuring that product pages are optimized with relevant keywords and high-quality images.
Example: Using descriptive product titles and detailed descriptions with keywords like “organic cotton t-shirt.”
Category Page Optimization
Optimizing category pages to help users and search engines find products easily.
Example: Creating categories with relevant keywords, like “summer dresses” and including descriptive text.
Site Search Optimization
Improving internal search functionality to help users find products.
Example: applying a search bar with autocomplete suggestions.
Shopping Cart Optimization
Making the checkout process smooth and user-friendly.
Example: Reducing the number of steps in the checkout process and offering multiple payment options.
Conversion Rate Optimization
Enhancing elements of the site to increase the percentage of visitors who make a purchase.
Example: Using A/B testing to find the most effective call-to-action buttons.
Strategies: Regularly update product listings, optimize product images, and use customer reviews to build trust.
Content SEO
Content SEO involves optimizing content to rank higher in search engine results and drive relevant traffic.
Key Elements:
Keyword Research
Finding and using relevant keywords that your target audience is searching for.
Example: Using tools like Google Keyword Planner to identify keywords for a blog post on “home workout routines.”
Content Creation
Writing high-quality, engaging, and informative content.
Example: Creating a comprehensive guide on “How to Start a Home Garden.”
Content Promotion
Sharing your content through various channels to increase visibility.
Example: Promoting a new blog post on social media and through email newsletters
Content Optimization
Enhancing content to improve its SEO performance.
Example: Adding internal links, optimizing headings, and using keywords naturally.
Best Practices: Create valuable content, optimize for relevant keywords, and promote through multiple channels.
White Hat SEO, Black Hat SEO, and Grey Hat SEO
White Hat SEO
White hat SEO refers to Righteous SEO practices that follow the guidelines set by search engines. These techniques focus on improving the user experience and creating value for visitors, without attempting to manipulate or deceive search engines.
Key Characteristics:
Adherence to Guidelines
White Hat SEO practices follow search engine guidelines, Especially those of Google. This means avoiding techniques that are deemed manipulative or false.
Focus on Quality
highlights creating high-quality content, building high-quality backlinks, and providing a good user experience.
Sustainable Results
White Hat techniques aim for long-term results by building a solid foundation for SEO that can resist algorithm updates.
Examples:
High-Quality Content Creation
Writing informative, engaging, and original content that provides real value to users. For instance, a well-researched blog post that answers common questions in your industry.
Natural Link Building
gaining backlinks from respected sources through guest blogging, partnerships, and creating shareable content. For example, a tech blog earns links from tech news sites by producing in-depth reviews.
On-Page Optimization
Properly optimizing title tags, meta descriptions, and headers. For instance, using relevant keywords in your meta descriptions to Faithfully reflect the page’s content.
Benefits
Compliance with Search Engine Guidelines:
Reduces the risk of damages or deindexing.
Long-Term Success:
Builds a credible and authoritative online business.
Enhanced User Experience
Focuses on providing value, leading to better engagement and satisfaction.
Black Hat SEO
Black Hat SEO refers to bad practices that violate search engine guidelines to manipulate rankings. These techniques often focus on exploiting shortcuts and loopholes rather than creating value for customers.
Key Characteristics:
Violation of Guidelines
Employs tactics that go against search engine rules, which can lead to damage or banning from search results.
Short-Term Gains
goals for quick improvements in rankings but often at the expense of long-term sustainability.
Risk of Penalties
The use of manipulative techniques can result in severe damage from search engines, including deindexing.
Examples:
Keyword Stuffing
Overloading a webpage with keywords to manipulate search rankings. For example, repeating the keyword “cheap running shoes” overly in a product description.
Hidden Text
Adding text that is not visible to users but readable by search engines, often by making it the same color as the background. For example, hiding a list of keywords in white text on a white background.
Link Farms
Creating or participating in networks of sites that link to each other for the sole purpose of boosting link metrics. For instance, a network of low-quality sites links to each other to artificially inflate link popularity.
Consequences:
Search Engine Penalties
This can lead to a significant drop in rankings or complete removal from search engine indexes.
Loss of Trust
Damage to your site’s reputation and credibility with users and search engines.
Short-Term Gains, Long-Term Risks
Opening boosts in rankings often lead to long-term damage if penalties are applied.
Grey Hat SEO
Definition: Grey Hat SEO refers to techniques that are not clearly defined as either ethical or unethical. These methods often lie in a gray area between White Hat and Black Hat practices, potentially pushing the boundaries of search engine guidelines without explicitly violating them.
Key Characteristics:
Ambiguous Practices
Techniques that may be considered questionable but do not clearly violate search engine guidelines.
Potential Risks
While not explicitly banned, these practices can still carry risks if they are deemed manipulative or if search engine algorithms change.
Uncertain Outcomes
Results from Grey Hat SEO can be unpredictable, with potential benefits and risks.
Examples:
Aggressive Link Building
Using approaches like “link exchanges” or buying links from low-quality sites that aren’t necessarily against guidelines but may be seen as manipulative. For example, exchanging links with multiple sites to boost SEO.
Content Scraping
Using content from other sources with slight modifications. For instance, republishing articles with minor changes can sometimes be a gray area if the content is not enough original.
Automated SEO Tools
using tools to generate backlinks or optimize content in ways that might be seen as manipulative. For example, using automated software to create large volumes of backlinks quickly.
Risks:
Penalties
Even if not immediately penalized, Grey Hat techniques can lead to future issues if search engines update their algorithms or change their policies.
Reputation Damage
Reputation can suffer if practices are perceived as deceptive or manipulative.
Conclusion
SEO covers several key areas: On-Page, Off-Page, Technical, Local, E-commerce, and Content SEO. Each area is important for enhance your site’s visibility and ranking. Using a mix of these techniques leads to better overall results. For more information, check out the Moz Blog for tips, Google’s SEO Starter Guide for basics, and SEMrush Academy for detailed courses and tools.
Learn SEO and get help from our experts.
Have questions? Don’t hesitate to Comment.
Q: What are the main types of SEO?
A: There are three primary types of SEO: * On-Page SEO: Optimizing elements within your website (title tags, meta descriptions, header tags, keyword optimization, content quality, image optimization, internal linking). * Off-Page SEO: Building your website’s authority through external factors (link building, social media marketing, online directories, guest posting, influencer marketing, brand mentions). * Technical SEO: Enhancing your website’s technical aspects for better performance and indexing (website speed, mobile-friendliness, XML sitemaps, robots.txt, structured data, crawl budget, indexation).
Q: What is the difference between White Hat, Black Hat, and Grey Hat SEO?
A: * White Hat SEO: Follows search engine guidelines, focusing on creating value for users (e.g., high-quality content, natural link building). * Black Hat SEO: Violates search engine guidelines, using manipulative techniques (e.g., keyword stuffing, hidden text, link farms). * Grey Hat SEO: Lies between White Hat and Black Hat, using questionable techniques that may or may not violate guidelines (e.g., aggressive link building, content scraping, automated SEO tools).
Q: What are some useful SEO tools?
A: Several SEO tools can help you analyze your website’s performance, research keywords, and track your progress. Popular options include Google Search Console, Google Analytics, SEMrush, Ahrefs, Moz, and Yoast SEO.
Q: What is schema markup?
A: Schema markup is code added to your website to help search engines understand your content better. It can improve your website’s appearance in search results.
Q: How can I build high-quality backlinks?
A: Building high-quality backlinks involves creating valuable content that attracts natural links from other websites. Focus on building relationships with other websites in your industry and participating in guest posting opportunities.